Manual Transaction Management
Beekeeper's Manual Transaction Mode allows you to ensure that you have full control over when transactions are committed, while also ensuring that you don't leave any transactions open by accident.
You will find this option in the bottom left of the SQL Editor
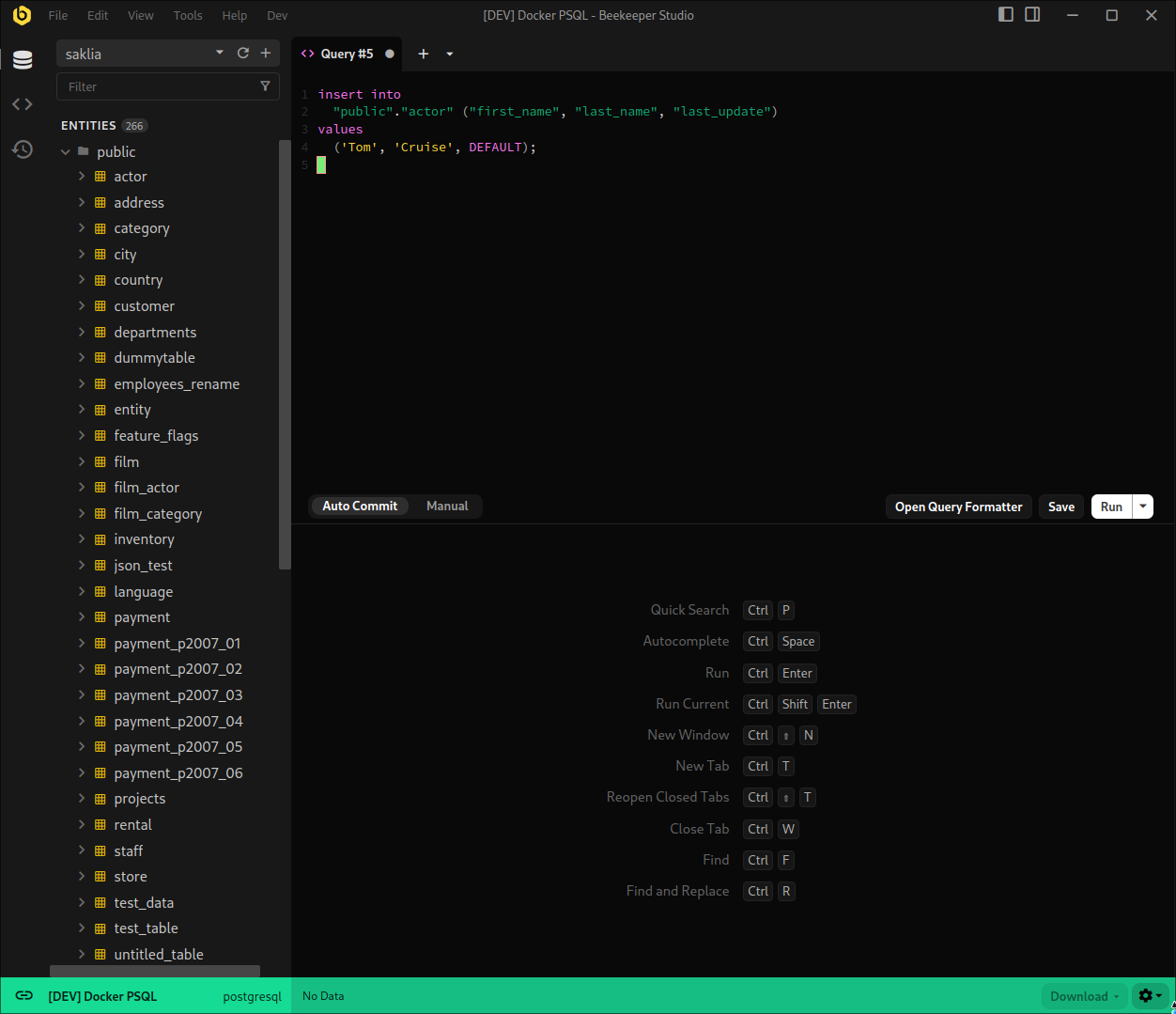
Begin Transaction
Once you have entered this mode, every query will be within a transaction and must be committed or rolled back for those changes to be reflected in your database. You can start a transaction by clicking the Begin button in the bottom left of the editor, or just by simply running a query, in which case Beekeeper will automatically prepend a begin statement to your query.
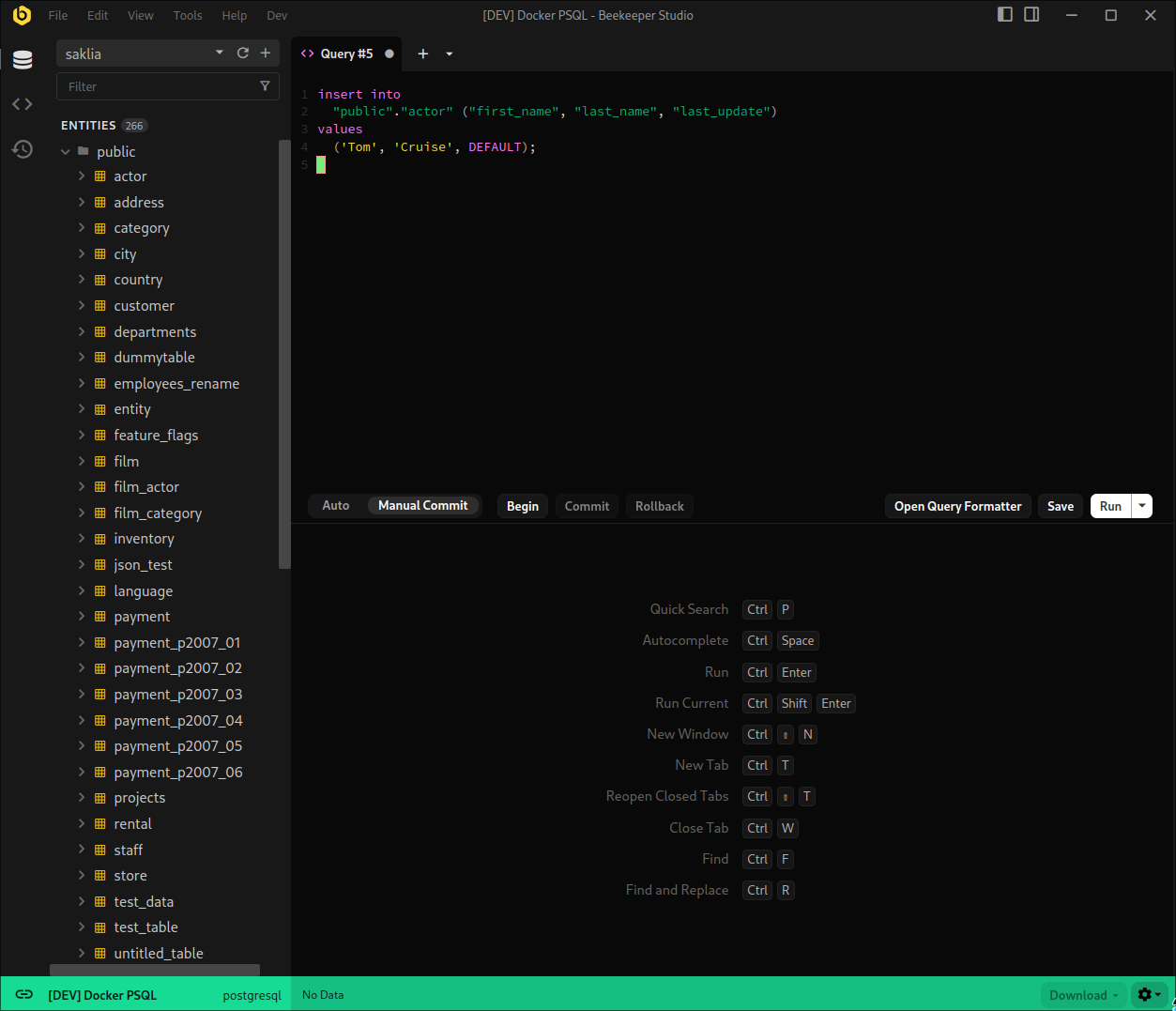
Active Transactions
When a transaction begins, we reserve a connection for that tab so that no context is lost, and you will have access to the Commit and Rollback buttons. As a precaution, there is also a timeout set for all transactions. The default is 10 minutes, with a 1 minute warning period. This means that by default, after 9 minutes you will get notified that a transaction is still open, and you will be told to finish the transaction, or keep it alive for another 10 minutes.
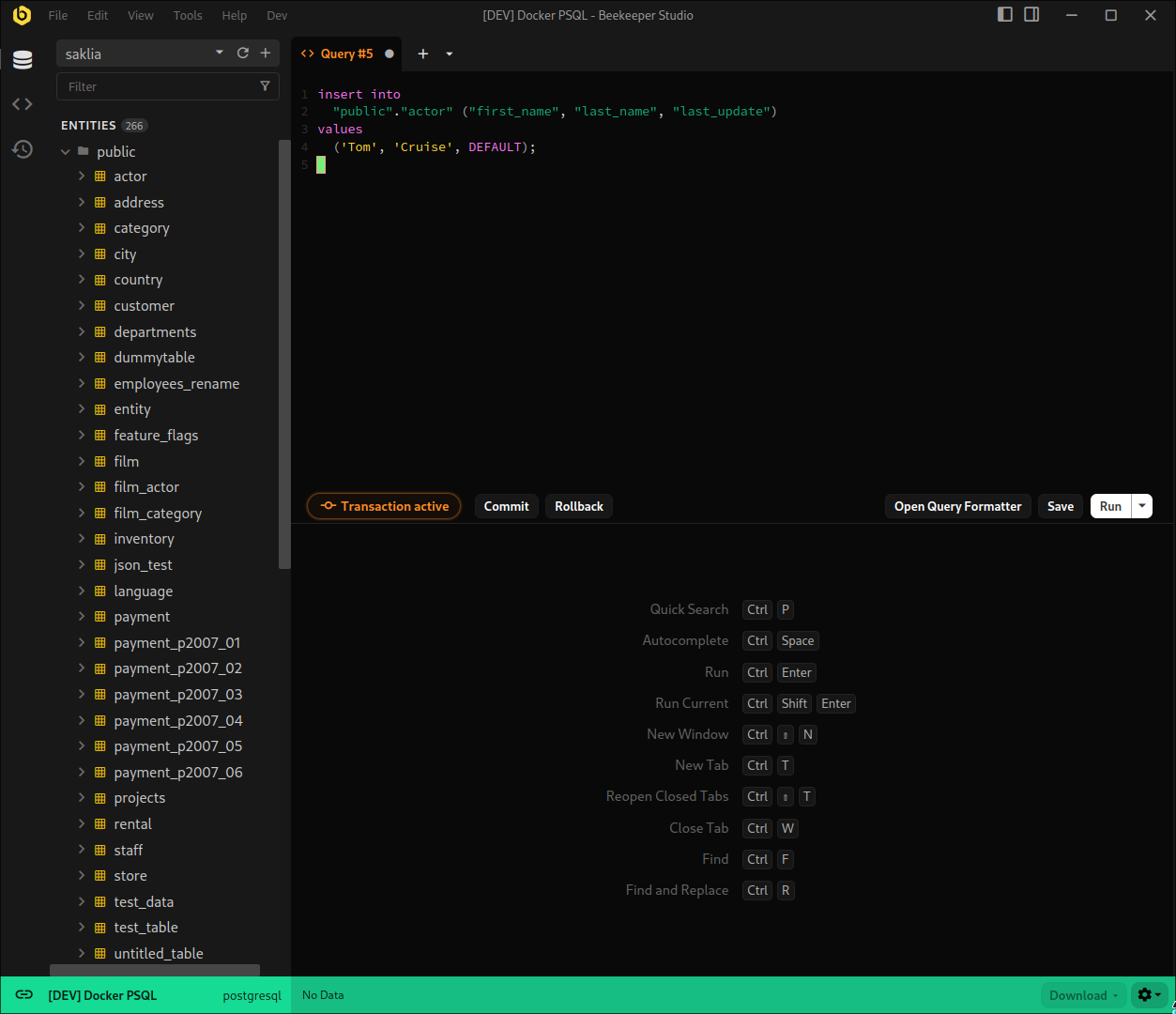
Configuration
You can change some of the defaults for this system using the config file (for every database, or just a specific database system).
[db.default]
; Max number of manual transactions to allow at a time
; This should be kept below the max pool size for the database, as these connections
; are pulled from that pool
maxReservedConnections = 2 ; Allow two active transactions at a time
; How long to keep a transaction open without any activity before automatically rolling it back in manual commit mode
manualTransactionTimeout = 600000 ; 10 Minutes
; The amount of time before an automatic rollback to warn the user that it is about to happen
autoRollbackWarningWindow = 60000 ; 1 Minute
[db.postgres]
maxReservedConnections = 4 ; Allow 4 active transactions at a time (only for postgres)
This functionality is currently only available for Postgres, CockroachDB, Redshift, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLServer, Firebird, and Oracle.